Title: Figure’s Humanoid Robot Advances in Manufacturing Training with BMW Partnership
Figure’s silver humanoid robot is making notable strides in its manufacturing training nearly six months after partnering with BMW. The recent video release highlights the robot’s growing capabilities, emphasizing the potential for AI-powered humanoids in industrial applications. This development marks a significant step forward in the integration of advanced robotics into manufacturing environments.
The Rise of AI-Powered Humanoid Robots The field of AI-powered humanoid robots is witnessing a surge in development, with numerous companies striving to create versatile machines capable of performing a broad range of tasks traditionally handled by humans. These robots aim to offer a more cost-effective and consistent labor source, potentially revolutionizing economic growth and labor markets. By creating a workforce adaptable to various tasks, the ultimate goal is to decouple economic progress from population growth and provide a labor source constrained only by available resources.
Figure’s Humanoid: Key Features and Capabilities Figure’s humanoid robot, designed for manufacturing tasks, stands 5 feet 6 inches tall and weighs approximately 132 pounds. It can carry up to 44 pounds, operates on an electric system, and runs continuously for five hours, reaching speeds of up to 2.7 mph. These specifications allow the robot to perform meaningful work in manufacturing settings while maintaining a form factor similar to human workers.
- Height: 5 feet 6 inches
- Weight: 132 pounds
- Payload Capacity: 44 pounds
- Operation Time: 5 hours
- Max Speed: 2.7 mph
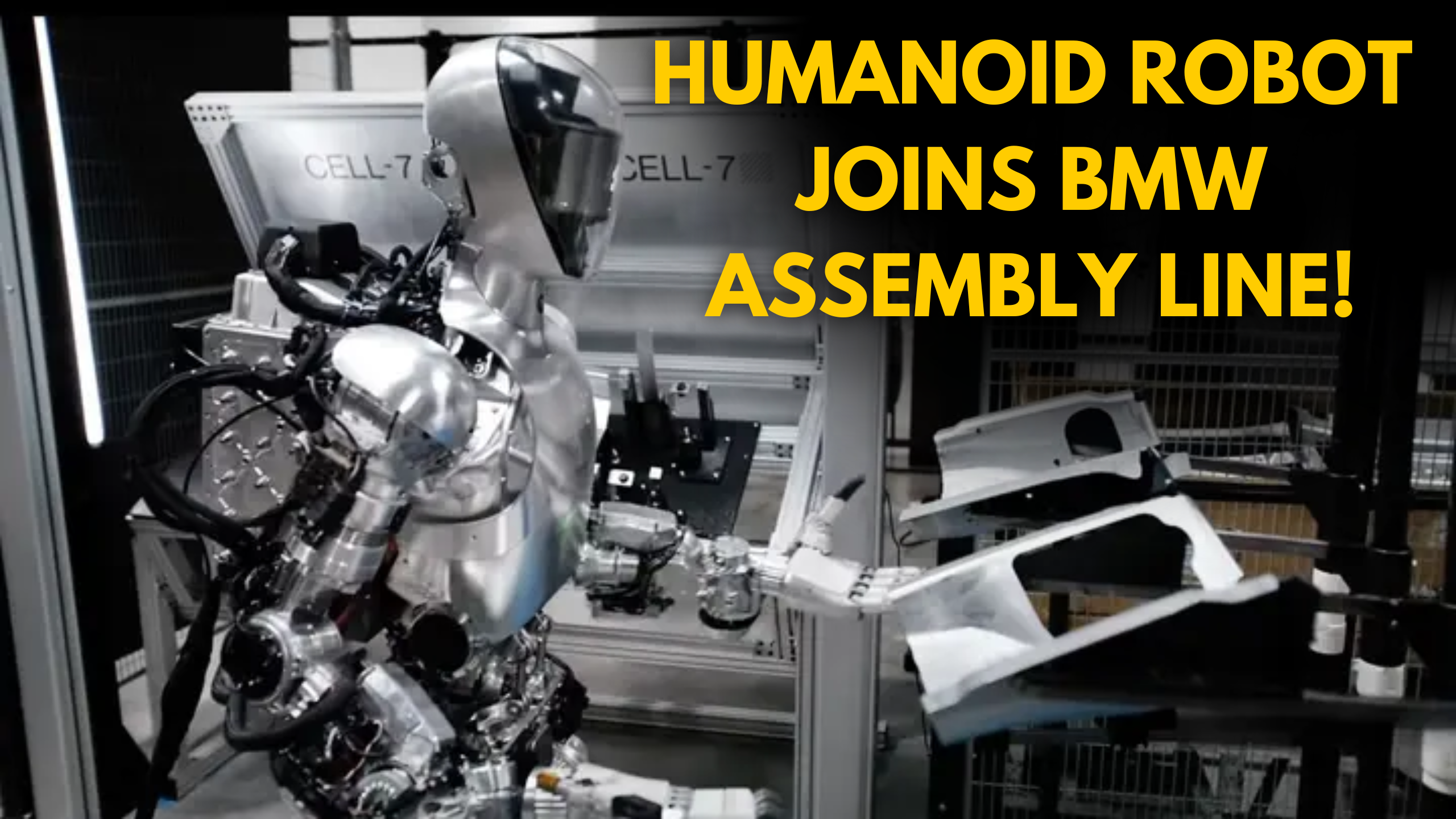
BMW Partnership: A Milestone for Figure The collaboration between Figure and BMW marks a major milestone for the robotics startup, representing its first commercial deal since its founding in 2022. This partnership demonstrates the growing interest in humanoid robotic solutions within the industry. The robots will be deployed at BMW’s Spartanburg facility in South Carolina, the largest automotive exporter in the U.S., which employs 11,000 people. Over the next 12 to 24 months, these robots will be integrated into various processes, including body shop operations, sheet metal work, and warehouse tasks.
Training Progress: The ‘BMW Full Use Case’ The latest demonstration, known as the “BMW Full Use Case,” showcases significant advancements in the Figure robot’s capabilities. The robot now excels in handling complex shapes, navigating obstacles, precise part placement, and self-correction. Notably, it can grasp and place large, intricate parts accurately, even with obstructed views, and can correct errors by adjusting parts with the back of its hand.
- Key Training Capabilities:
- Grasping Complex Shapes
- Navigating Obstacles
- Precision Placement of Parts
- Error Correction and Fine-Tuning
Challenges and Competition The field of humanoid robots is competitive, with several companies developing similar technologies. Apptronik is partnering with Mercedes to trial its Apollo robot, while Boston Dynamics continues to enhance its Atlas robot for various applications, including automotive manufacturing. Tesla, with its extensive car production facilities, is also developing its Optimus robot. Each company’s approach varies, contributing to a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector in humanoid robotics.
The Future of Humanoid Robots in Manufacturing As AI models advance, humanoid robots are expected to exhibit faster and smoother movements and acquire new skills more quickly. Their integration into manufacturing environments is anticipated to grow, potentially transforming production processes across industries. However, this technological advancement brings economic, ethical, and societal implications, including job displacement and new skill requirements. Balancing innovation with human employment and well-being will be crucial as the industry evolves.
Economic and Societal Implications
- Job Displacement: The potential for automation to replace human jobs.
- New Skill Requirements: The need for workers to acquire new skills to adapt to changing job roles.
- Ethical Considerations: The impact of robots on labor markets and ethical concerns about automation.
Conclusion The development of general-purpose humanoid robots, exemplified by Figure’s collaboration with BMW, represents a transformative technology for manufacturing and beyond. While the robot is still in early stages, the progress showcased in the BMW partnership is promising. For humanoid robots to revolutionize the workforce, they must demonstrate clear economic advantages over human workers, including efficiency, adaptability, and safety in real-world environments.
Read More: OSTP Media | Tech, Auto, and Trending News